Моллю́ски, или мягкоте́лые (лат. Mollusca), — тип первичноротых целомических животных со спиральным дроблением. Оценка общего количества видов моллюсков колеблется в разных публикациях в диапазоне от 100 до 200 тысяч. В России насчитывают . Этот тип обычно делят на 7 или 8 современных классов, к которым добавляют минимум 3 полностью вымерших. Моллюски освоили практически все среды обитания: морские и пресноводные водоёмы, почву, наземно-воздушную среду. Некоторые моллюски стали временными или постоянными паразитами других животных.

А́дский вампи́р, или адский кальмар-вампир , — небольшой глубоководный головоногий моллюск-детритофаг из семейства Vampyroteuthidae, выделяемый в монотипический род Vampyroteuthis, обитающий в умеренных и тропических водах мирового океана. Это единственный известный науке головоногий моллюск, проводящий всю жизнь на глубинах 400—1000 м в зоне с минимальным количеством растворённого в воде кислорода. Благодаря наличию уникальных втягивающихся чувствительных бичевидных филаментов, его выделяют в отряд вампироморфов (Vampyromorpha), имеющий общие черты как с кальмарами, так и с осьминогами.

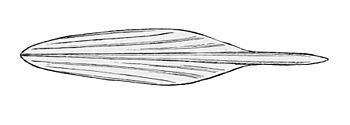
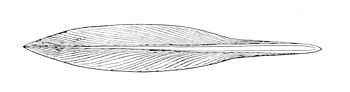
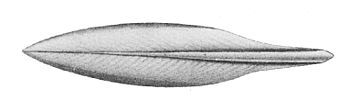
Кальма́ры (лат. Teuthida) — ранее выделявшийся отряд десятируких головоногих моллюсков. Тело представителей группы обтекаемой цилиндрической формы с двумя треугольными боковыми плавниками, обычно заостренное на заднем конце. Голова чётко отделена от туловища, на ней расположены щупальца с присосками и крючками. Из них восемь — это обычно короткие конической формы и два длинные с расширениями на конце. Длина тела от 0,7 см до более 5 м, с учётом щупальцев общая длина может превышать эти размеры в несколько раз. Раковина внутренняя, в виде узкой роговой пластинки. У всех представителей группы имеется радула для соскребания и размельчения пищи, и чернильная железа. Секрет, выделяемый ею, окрашивает воду и скрывает кальмаров при нападении хищников. Плавают при помощи плавников и реактивно — резко выбрасывают воду из своей мантийной полости через воронку, поворачивая которую они способны маневрировать, двигаться назад и вперед. Яйца откладываются в капсулах, реже по одному, в воду или на дно. Известно более 250 видов. Наиболее многочисленны и разнообразны в тропических водах. В дальневосточных и северных морях в России обитает свыше 30 видов. Встречаются как в поверхностных слоях, так и на больших глубинах. Некоторые виды совершают дальние нагульные и нерестовые миграции. Способны развивать большую скорость, например, при охоте на добычу или спасаясь от хищников. Ряд видов могут изменять окраску. Мелкие планктонные виды отличаются слабо развитой мускулатурой и студенистым телом, а свою плавучесть регулируют, изменяя концентрации хлорида аммония в своём теле. Глубоководные виды часто прозрачные или окрашены в тёмно-красные тона, многие обладают органами свечения (фотофоры). Кальмары служат пищевой базой для многих рыб, зубатых китов, морских птиц. Являются объектом промысла, занимая по объёму вылова первое место среди всех групп моллюсков. Используются человеком в пищу, служат сырьем для фармакологической промышленности и парфюмерии.

Головоно́гие, или цефалопо́ды (лат. Cephalopoda, от др.-греч. ϰεφαλή — голова и πόδι — нога), — класс моллюсков, характеризующийся двусторонней симметрией и 8, 10 или большим количеством щупалец вокруг головы, развившихся из «ноги» моллюсков. Головоногие стали доминирующей группой моллюсков во время ордовикского периода и были представлены примитивными наутилоидами. Известно 2 современных подкласса: двужаберные (Coleoidea), который включает в себя осьминогов, кальмаров, каракатиц, и наутилоидеи (Nautiloidea), представленные наутилусами (Nautilus) и Allonautilus. У представителей подкласса двужаберных раковина редуцирована, либо полностью отсутствует, тогда как у представителей наутилоидей внешняя раковина остаётся. Головоногие имеют наиболее совершенную из беспозвоночных кровеносную систему и наиболее развитую нервную систему. Описано приблизительно 800 современных видов, в России — 70 видов. Самые известные из вымерших групп: Ammonoidea (аммониты) и Belemnitida (белемниты), а из современных: кальмары, каракатицы и осьминоги.

Белемни́ты или белемнитиды (лат. Belemnitida, от др.-греч. βέλεμνον — «метательный снаряд»), — отряд вымерших головоногих моллюсков из подкласса двужаберных. Хищники, вероятно, хорошо плавали; имели плавники, крупные глаза, роговые челюсти и чернильный мешок. На щупальцах были крючки. Внутри тела белемнита был массивный карбонатный ростр, похожий на наконечник стрелы. С этими рострами, часто встречающимися в мезозойских отложениях, и связано название отряда.

Наутилоиде́и (лат. Nautiloidea) — подкласс головоногих моллюсков. Имеют наружную раковину, подразделённую на камеры. Ископаемые представители известны с палеозоя. Хотя наутилоидеи состоят в родстве с аммонитами и внешне схожи с ними, периоды их расцвета не совпадали.

Десятиру́кие (лат. Decapodiformes) — надотряд головоногих моллюсков из подкласса двужаберных (Coleoidea). Представители обладают пятью парами рук, четвёртая из которых преобразована в ловчие щупальца. Располагающиеся на руках присоски вооружены крючьями.

Двужаберные, или колеоиды (лат. Coleoidea), — подкласс головоногих моллюсков (Cephalopoda). Включают подавляющее большинство современных представителей класса, в том числе кальмаров, каракатиц (Sepiida) и осьминогов (Octopoda).

Nectocaris pteryx (лат.) — вид вымерших животных неясного систематического положения, единственный в роде Nectocaris и семействе Nectocarididae. Жили в морях кембрийского периода.
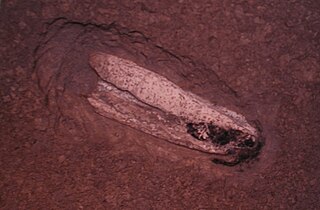
Teudopsis (лат.) — род вымерших головоногих моллюсков из отряда вампироморфов (Vampyromorpha). Известны по ископаемым гладиусам в отложениях тоарского яруса нижней юры. На спинной стороне гладиуса имеется хорошо развитый киль. Найдены в канадской провинции Альберта и Европе. Родственными родами являются Trachyteuthis и Glyphiteuthis. Представители рода обитали в платформенных морях.

Moroteuthopsis longimana (лат.) — вид крупных кальмаров из семейства Onychoteuthidae. Его мантия достигает длины по меньшей мере 85 см, а прижизненные её размеры оцениваются как 1,15 м. Самый большой целый экземпляр кальмаров этого вида с полной длиной в 2,3 м был пойман в Антарктике в 2000 году. Полярная акула и атлантическая сельдевая акула охотятся на Moroteuthopsis longimana. Он составляет около 21 % и 19 % от общей массы головоногих, поглощаемой этими акулами.

Rossia moelleri (лат.) — вид головоногих моллюсков рода Rossia из семейства сепиолиды (Sepiolidae).

Оммастрефиды, или летающие кальмары (лат. Ommastrephidae), — семейство головоногих моллюсков из отряда океанических кальмаров (Oegopsida), содержащее три подсемейства, 11 родов и более 20 видов. Они широко распространены во всем мире и широко вылавливаются в качестве пищи. Один из видов, тихоокеанский кальмар, составляет половину всего улова головоногих моллюсков в мире.

Todarodes — род головоногих моллюсков из отряда десятируких семейства Ommastrephidae. Входит в подсемейство Todarodinae, для которого является типовым родом. Род содержит пять видов, которые частично аллопатричны, но при этом их ареалы охватывают большую часть Мирового океана. Являются ценными промысловыми моллюсками. Один из видов, Todarodes pacificus, составляет половину всего улова головоногих моллюсков в мире.

Todarodinae (лат.) — подсемейство головоногих моллюсков из отряда десятируких семейства Ommastrephidae. Типовой род — Todarodes. Ареал представителей подсемейства охватывают большую часть Мирового океана. Являются ценными промысловыми моллюсками. Один из видов, Todarodes pacificus, составляет половину всего улова головоногих моллюсков в мире.

Ommastrephinae (лат.) — подсемейство головоногих моллюсков семейства Ommastrephidae из надотряда десятируких. Типовой род — Ommastrephes.

Ornithoteuthis (лат.) — род головоногих моллюсков из семейства Ommastrephidae. Включает два вида. Это относительно небольшие кальмары с длиной мантии около 100—200 мм, очень подвижные и довольно необычные. Характеристики, которые отличают их от других представителей подсемейства Ommastrephinae, заключаются в том, что их мантия и плавники вытянуты в узкий хвост, и у них есть светящаяся полоса вдоль средней линии на внутренностях. Один вид, Ornithoteuthis antillarum, встречается в теплых водах Атлантического океана, а другой, Ornithoteuthis volatilis, в аналогичных областях Индо-Тихоокеанской области, они состоят в близком родстве и, как считается, возникли в результате относительно недавнего видообразования.

Loligo forbesii (лат.) — вид головоногих моллюсков из семейства Loliginidae.

Syllipsimopodi bideni (лат.) — ископаемый вид головоногих моллюсков, единственный в составе рода Syllipsimopodi из отряда вампироморфов (Vampyromorpha). Известен по отпечаткам из штата Монтана, США, возрастом около 330—323 млн лет . S. bideni назван в честь президента США Джо Байдена и для повышения осведомленности о его политике в области изменения климата.

Интеллект головоногих измеряет уровень когнитивных способностей класса головоногих моллюсков.