EED
| Эмбриональное развитие эктодермы | |||
|---|---|---|---|
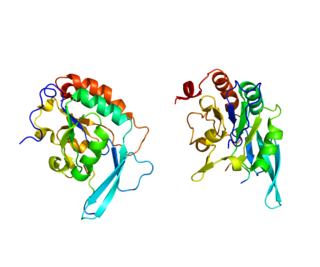
 Представлено на основе PDB 3IIW. Представлено на основе PDB 3IIW. | |||
| Доступные структуры | |||
| PDB | Поиск ортологов: PDBe, RCSB | ||
| Идентификаторы | |||
| Символ | EED ; HEED; WAIT1 | ||
| Внешние ID | OMIM: 605984 MGI: 95286 HomoloGene: 2814 IUPHAR: GeneCards: Ген EED | ||
| Профиль экспрессии РНК | |||
 | |||
 | |||
| Больше информации | |||
| Ортологи | |||
| Вид | Человек | Мышь | |
| Entrez | 8726 | 13626 | |
| Ensembl | ENSG00000074266 | ENSMUSG00000030619 | |
| UniProt | O75530 | Q921E6 | |
| RefSeq (мРНК) | NM_003797 | NM_021876 | |
| RefSeq (белок) | NP_003788 | NP_068676 | |
| Локус (UCSC) | Chr 11: 85.96 – 85.99 Mb | Chr 7: 89.95 – 89.98 Mb | |
| Поиск в PubMed | Искать | Искать | |
Белок группы Polycomb EED (эмбрионального развития эктодермы) (англ. Polycomb protein EED) — белок, кодируемый у человека геном EED[1][2][3].
Функции
Белок Polycomb EED является членом семейства Polycomb (PcG). Члены семейства PcG образуют многомерные белковые комплексы, которые участвуют в поддержании транскрипционно-репрессивного состояния генов в ходе последовательных клеточных поколений. Этот белок взаимодействует с усилителем zeste 2, цитоплазматическим хвостом интегрина β7, белком MА вируса иммунодефицита типа 1 (ВИЧ-1) и гистондеацетилазами. Этот белок опосредует подавление активности генов гистонов посредством деацетилирования и может выступать в качестве специфичного регулятора функции интегрина. Для этого гена были определены два варианта транскриптов, кодирующих различные изоформы[3].
Клиническое значение
У человека мутация de novo[англ.] в EED, как сообщалось, приводит к развитию симптомов, напоминающих синдром Уивера[4].
Взаимодействия с другими белками
EED, как было выявлено, взаимодействует с:
Примечания
- ↑ 1 2 Rietzler M., Bittner M., Kolanus W., Schuster A., Holzmann B. The human WD repeat protein WAIT-1 specifically interacts with the cytoplasmic tails of beta7-integrins. (англ.) // The Journal of biological chemistry. — 1998. — Vol. 273, no. 42. — P. 27459—27466. — PMID 9765275.
- ↑ Schumacher A., Lichtarge O., Schwartz S., Magnuson T. The murine Polycomb-group gene eed and its human orthologue: functional implications of evolutionary conservation. (англ.) // Genomics. — 1998. — Vol. 54, no. 1. — P. 79—88. — doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5509. — PMID 9806832.
- ↑ 1 2 Entrez Gene: EED embryonic ectoderm development.
- ↑ Cohen A. S., Tuysuz B., Shen Y., Bhalla S. K., Jones S. J., Gibson W. T. A novel mutation in EED associated with overgrowth. (англ.) // Journal of human genetics. — 2015. — doi:10.1038/jhg.2015.26. — PMID 25787343.
- ↑ 1 2 3 van der Vlag J., Otte A. P. Transcriptional repression mediated by the human polycomb-group protein EED involves histone deacetylation. (англ.) // Nature genetics. — 1999. — Vol. 23, no. 4. — P. 474—478. — doi:10.1038/70602. — PMID 10581039.
- ↑ van Lohuizen M., Tijms M., Voncken J. W., Schumacher A., Magnuson T., Wientjens E. Interaction of mouse polycomb-group (Pc-G) proteins Enx1 and Enx2 with Eed: indication for separate Pc-G complexes. (англ.) // Molecular and cellular biology. — 1998. — Vol. 18, no. 6. — P. 3572—3579. — PMID 9584197.
- ↑ Denisenko O., Shnyreva M., Suzuki H., Bomsztyk K. Point mutations in the WD40 domain of Eed block its interaction with Ezh2. (англ.) // Molecular and cellular biology. — 1998. — Vol. 18, no. 10. — P. 5634—5642. — PMID 9742080.
- ↑ Jin Q., van Eynde A., Beullens M., Roy N., Thiel G., Stalmans W., Bollen M. The protein phosphatase-1 (PP1) regulator, nuclear inhibitor of PP1 (NIPP1), interacts with the polycomb group protein, embryonic ectoderm development (EED), and functions as a transcriptional repressor. (англ.) // The Journal of biological chemistry. — 2003. — Vol. 278, no. 33. — P. 30677—30685. — doi:10.1074/jbc.M302273200. — PMID 12788942.
- ↑ Enünlü I., Pápai G., Cserpán I., Udvardy A., Jeang K. T., Boros I. Different isoforms of PRIP-interacting protein with methyltransferase domain/trimethylguanosine synthase localizes to the cytoplasm and nucleus. (англ.) // Biochemical and biophysical research communications. — 2003. — Vol. 309, no. 1. — P. 44—51. — PMID 12943661.
Литература
- Joseph A. M., Kumar M., Mitra D. Nef: "necessary and enforcing factor" in HIV infection. (англ.) // Current HIV research. — 2005. — Vol. 3, no. 1. — P. 87—94. — PMID 15638726.
- Van Maele B., Debyser Z. HIV-1 integration: an interplay between HIV-1 integrase, cellular and viral proteins. (англ.) // AIDS reviews. — 2005. — Vol. 7, no. 1. — P. 26—43. — PMID 15875659.
- Jones C. A., Ng J., Peterson A. J., Morgan K., Simon J., Jones R. S. The Drosophila esc and E(z) proteins are direct partners in polycomb group-mediated repression. (англ.) // Molecular and cellular biology. — 1998. — Vol. 18, no. 5. — P. 2825—2834. — PMID 9566901.
- van Lohuizen M., Tijms M., Voncken J. W., Schumacher A., Magnuson T., Wientjens E. Interaction of mouse polycomb-group (Pc-G) proteins Enx1 and Enx2 with Eed: indication for separate Pc-G complexes. (англ.) // Molecular and cellular biology. — 1998. — Vol. 18, no. 6. — P. 3572—3579. — PMID 9584197.
- Sewalt R. G., van der Vlag J., Gunster M. J., Hamer K. M., den Blaauwen J. L., Satijn D. P., Hendrix T., van Driel R., Otte A. P. Characterization of interactions between the mammalian polycomb-group proteins Enx1/EZH2 and EED suggests the existence of different mammalian polycomb-group protein complexes. (англ.) // Molecular and cellular biology. — 1998. — Vol. 18, no. 6. — P. 3586—3595. — PMID 9584199.
- Denisenko O., Shnyreva M., Suzuki H., Bomsztyk K. Point mutations in the WD40 domain of Eed block its interaction with Ezh2. (англ.) // Molecular and cellular biology. — 1998. — Vol. 18, no. 10. — P. 5634—5642. — PMID 9742080.
- Peytavi R., Hong S. S., Gay B., d'Angeac AD, Selig L., Bénichou S., Benarous R., Boulanger P. HEED, the product of the human homolog of the murine eed gene, binds to the matrix protein of HIV-1. (англ.) // The Journal of biological chemistry. — 1999. — Vol. 274, no. 3. — P. 1635—1645. — PMID 9880543.
- van der Vlag J., Otte A. P. Transcriptional repression mediated by the human polycomb-group protein EED involves histone deacetylation. (англ.) // Nature genetics. — 1999. — Vol. 23, no. 4. — P. 474—478. — doi:10.1038/70602. — PMID 10581039.
- Satijn D. P., Hamer K. M., den Blaauwen J., Otte A. P. The polycomb group protein EED interacts with YY1, and both proteins induce neural tissue in Xenopus embryos. (англ.) // Molecular and cellular biology. — 2001. — Vol. 21, no. 4. — P. 1360—1369. — doi:10.1128/MCB.21.4.1360-1369.2001. — PMID 11158321.
- Kuzmichev A., Nishioka K., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Reinberg D. Histone methyltransferase activity associated with a human multiprotein complex containing the Enhancer of Zeste protein. (англ.) // Genes & development. — 2002. — Vol. 16, no. 22. — P. 2893—2905. — doi:10.1101/gad.1035902. — PMID 12435631.
- Jin Q., van Eynde A., Beullens M., Roy N., Thiel G., Stalmans W., Bollen M. The protein phosphatase-1 (PP1) regulator, nuclear inhibitor of PP1 (NIPP1), interacts with the polycomb group protein, embryonic ectoderm development (EED), and functions as a transcriptional repressor. (англ.) // The Journal of biological chemistry. — 2003. — Vol. 278, no. 33. — P. 30677—30685. — doi:10.1074/jbc.M302273200. — PMID 12788942.
- Enünlü I., Pápai G., Cserpán I., Udvardy A., Jeang K. T., Boros I. Different isoforms of PRIP-interacting protein with methyltransferase domain/trimethylguanosine synthase localizes to the cytoplasm and nucleus. (англ.) // Biochemical and biophysical research communications. — 2003. — Vol. 309, no. 1. — P. 44—51. — PMID 12943661.
- Violot S., Hong S. S., Rakotobe D., Petit C., Gay B., Moreau K., Billaud G., Priet S., Sire J., Schwartz O., Mouscadet J. F., Boulanger P. The human polycomb group EED protein interacts with the integrase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. (англ.) // Journal of virology. — 2003. — Vol. 77, no. 23. — P. 12507—12522. — PMID 14610174.
- Witte V., Laffert B., Rosorius O., Lischka P., Blume K., Galler G., Stilper A., Willbold D., D'Aloja P., Sixt M., Kolanus J., Ott M., Kolanus W., Schuler G., Baur A. S. HIV-1 Nef mimics an integrin receptor signal that recruits the polycomb group protein Eed to the plasma membrane. (англ.) // Molecular cell. — 2004. — Vol. 13, no. 2. — P. 179—190. — PMID 14759364.
- Cao R., Zhang Y. SUZ12 is required for both the histone methyltransferase activity and the silencing function of the EED-EZH2 complex. (англ.) // Molecular cell. — 2004. — Vol. 15, no. 1. — P. 57—67. — doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2004.06.020. — PMID 15225548.
- Pasini D., Bracken A. P., Jensen M. R., Lazzerini Denchi E., Helin K. Suz12 is essential for mouse development and for EZH2 histone methyltransferase activity. (англ.) // The EMBO journal. — 2004. — Vol. 23, no. 20. — P. 4061—4071. — doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600402. — PMID 15385962.