Micheleidae
| Micheleidae | |
|---|---|
 Tethisea indica | |
| Научная классификация | |
Домен: Царство: Подцарство: Без ранга: Без ранга: Без ранга: Без ранга: Тип: Подтип: Класс: Подкласс: Надотряд: Отряд: Подотряд: Инфраотряд: Семейство: Micheleidae | |
| Международное научное название | |
| Micheleidae Sakai, 1992[1] | |
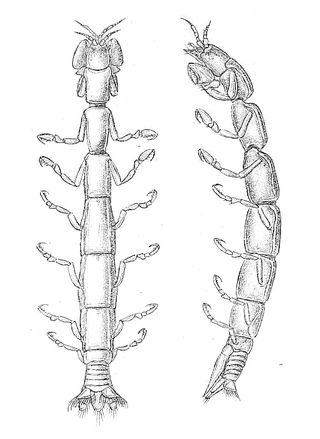
Micheleidae (лат.) — семейство десятиногих ракообразных (Axiidea, Decapoda)[2].
Описание
Цефалоторакс латерально сжатый, оканчивающийся в середине заднего края в виде срединной доли, отделённой от выпуклых заднебоковых краёв карапакса, которые утолщены и образуют маргинальный гребень. Рострум плоский или редуцирован, апикально острый, с боковыми килями. Первая и вторая пара переопод клешневидные. Линия талассиника отсутствует. Передняя часть головогруди, вторые—четвёртые пары переопод и первая-шестая пары плеомер с несколькими боковыми рядами щетинок[3][4][5].
Классификация
На май 2024 семейство включает 6 родов, половина из которых ископаемые. Группа была выделена в 1992 году в ранге подсемейства Micheleinae Sakai, 1992, а в 1993 году описано подсемейство Meticonaxiinae Sakai, 1993 (иногда рассматриваемое в ранге семейства Meticonaxiidae)[2][6][4][7].
- † Amatukamius Karasawa & Ohara, 2019[8]
- Marcusiaxius Rodrigues & de Carvalho, 1972[9]
- Meticonaxius de Man, 1905[10]
- =Metaxius Bouvier, 1905
- =Meteoraxius Sakai & Türkay, 2012[11]
- † Michelea Kensley & Heard, 1991[12]
- =Micheleopsis Sakai, 2010[13]
- Paki Karasawa & Hayakawa, 2000[14]
- † Tethisea Poore, 1994[15]
Примечания
- ↑ Sakai, K. (1992). The families Callianideidae and Thalassinidae, with the description of two new subfamilies, one new genus and two new species (Decapoda, Thalassinidea). Naturalists, Publications of Tokushima Biological Laboratory, Shikoku University. 4: 1—33.
- ↑ 1 2 Семейство Micheleidae (англ.) в Мировом реестре морских видов (World Register of Marine Species). (Дата обращения: 6 июня 2024).
- ↑ Dworschak P. C., Felder D. L., Tudge Ch. C. Infraorders Axiidea de Saint Laurent, 1979 and Gebiidea de Saint Laurent, 1979 (formerly known collectively as Thalassinidea) // Decapoda: Astacidea P.P. (Enoplometopoidea, Nephropoidea), Glypheidea, Axiidea, Gebiidea, and Anomura (англ.) / Frederick Schram and Carel von Vaupel Klein (Eds). — BRILL, 2012. — P. 109–219. — 359 p. — (Treatise on Zoology - Anatomy, Taxonomy, Biology. The Crustacea, Volume 9 Part B.). — ISBN 978-90-47-43017-9. — doi:10.1163/9789047430179_004.
- ↑ 1 2 Sakai K. Axioidea of the World and a Reconsideration of the Callianassoidea (Decapoda, Thalassinidea, Callianassida) (англ.). — BRILL, 2011. — 616 p. — (Crustaceana Monographs, 13). — ISBN 978-90-47-42418-5. — doi:10.1163/9789047424185.
- ↑ Sakai, K. (2017). Descriptions of eight species from the superfamilies Axioidea Huxley, 1879 and Callianassoidea Dana, 1852, with a revised key to the species of the genus Acanthaxius Sakai & De Saint Laurent, 1989 (Decapoda, Callianassidea). Crustaceana. 90(2): 177—197. https://doi.org/10.1163/15685403-00003621
- ↑ Micheleidae. gbif.org
- ↑ Poore, G.C.B. & Collins, D.J. (2015). Micheleidae (Crustacea: Decapoda: Axiidea): new family, generic and species synonymies, three new Australian species, and new records. Memoirs of Museum Victoria. 73: 95—105., http://museumvictoria.com.au/pages/373635/095-105_mmv73_poore2_2_web.pd
- ↑ Karasawa, H.; Ohara, M. (2019). Establishment of a new genus for Callianassa (s.l.) sakakuraorum Karasawa, 2000 (Decapoda: Axiidea). Bulletin of the Mizunami Fossil Museum. 45: 33—42
- ↑ Rodrigues, S. de A.; de Carvalho, H.A. (1972). Marcusiaxius lemoscastroi, g. n., sp. n., primeira occurrência da família Axiidae (Crustacea, Decàpoda, Thalassinidea) no Brasil. Ciência e Cultura, Såo Paulo. 24 (Suplemento): 357.
- ↑ Poore, G.C.B. (1997). A review of the thalassinidean families Callianideidae Kossmann, Micheleidae Sakai, and Thomassiniidae de Saint Laurent (Crustacea: Decapoda) with descriptions of fifteen new species. Zoosystema. 19: 345—420.
- ↑ Sakai, K.; Türkay, M. (2012). A collection of Thalassinidea Latreille, 1831 (Decapoda, Pleocyemata) from the Senckenberg Forschungsinstitut and Natural History Museum, Frankfurt am Main. Crustaceana. 85: 723—765
- ↑ Kensley, B.; Heard, R.W. (1991). An examination of the shrimp family Callianideidae (Crustacea: Decapoda: Thalassinidea. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington. 104: 493—537.
- ↑ Sakai, K. (2010). Callianassoidea from the Gulf of Tonkin and the Red Sea, in the Zoological Museum of Moscow University (Decapoda, Thalassinidea). Crustaceana. 83 : 1431—1467.
- ↑ Karasawa, H.; Hayakawa, H. (2000). Additions to Cretaceous decapod crustaceans from Hokkaido, Japan. — Part 1. Nephropidae, Micheleidae and Galatheidae. Palaeontological Research. 4(2): 139—145.
- ↑ Poore, G.C.B. (1994) A phylogeny of the families of Thalassinidea (Crustacea: Decapoda) with keys to the families and genera. Memoirs of the Museum of Victoria, 54, 79—120.
Литература
- Sakai K. Callianassoidea of the world (Decapoda: Thalassinidea) (англ.). — BRILL, 2005. — 285 p. — (Crustaceana Monographs, 4). — ISBN 978-90-47-41689-0. — doi:10.1163/9789047416890.
- Sakai K. (1999). Synopsis of the family Callianassidae, with keys to subfamilies, genera, and species, and the description of new taxa (Crustacea: Decapoda: Thalassinidea). Zoologische Verhandelingen, Leiden, 326(30), 1—152.